In today’s fast-paced tech world, the term “cloud native DevOps” is more than just a buzzword—it’s the secret sauce for agile development. Imagine a world where deploying applications is as easy as ordering takeout. Enter Kubernetes, the superhero of container orchestration that’s transforming how teams deliver software. With its ability to scale seamlessly and manage complex applications, Kubernetes makes DevOps feel like a walk in the park—if that park had Wi-Fi and unlimited coffee.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Cloud Native DevOps
Cloud native DevOps encompasses practices and tools that enable developers to build, deploy, and manage applications in dynamic environments like Kubernetes. Using microservices architecture is a key aspect, promoting smaller, independent services that enhance agility and improve deployment efficiency.
Kubernetes plays a vital role by automating container orchestration, which simplifies scaling, management, and deployment of applications. Scalability in Kubernetes allows teams to adjust resources according to demand, making it easier to handle varying traffic loads. Efficient resource management drives operational excellence and optimizes costs.
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are integral to cloud native DevOps. Implementing CI/CD ensures that code changes are automatically tested and deployed, significantly reducing the time between feature development and production release. Additionally, automated testing enhances code quality through consistent feedback loops.
Collaboration among teams is critical in cloud native DevOps. Development and operations teams, often referred to as DevOps teams, work closely to enhance communication and streamline processes. This collaboration fosters a culture of shared responsibility, where everyone contributes to application reliability and performance.
Monitoring and observability are essential for maintaining application health in cloud native environments. Tools integrated within Kubernetes can track performance metrics and detect anomalies in real time. Proactive monitoring aids in swiftly identifying issues, allowing teams to address potential disruptions before they impact users.
Cloud native DevOps, powered by Kubernetes, streamlines software development through automation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. The approach focuses on delivering high-quality applications that meet user needs efficiently.
Introduction to Kubernetes
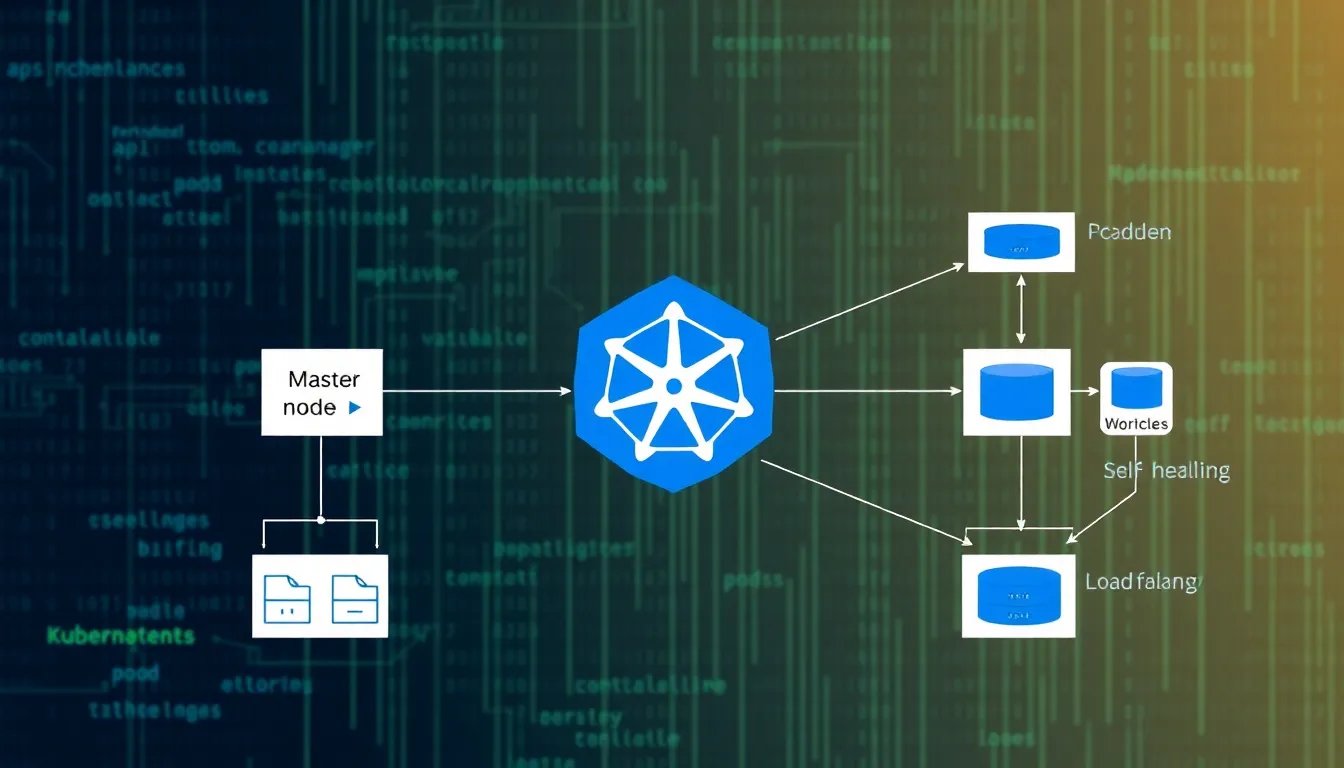
Kubernetes serves as a cornerstone for cloud native DevOps, enabling efficient application deployment and management in dynamic environments. With its container orchestration capabilities, teams can streamline processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Key Features of Kubernetes
Kubernetes offers several key features that empower teams. Scalability allows applications to adjust resources automatically based on demand. Self-healing capabilities enable automatic restarts and replacements of failed components. Load balancing distributes traffic evenly across resources, ensuring optimal performance under varying workloads. Service discovery streamlines communication between services, promoting seamless integration within applications. Moreover, the extensibility feature permits developers to customize and enhance the platform through various plugins and APIs.
Kubernetes Architecture
Kubernetes architecture comprises several components, each playing a vital role. The master node orchestrates the entire cluster, managing the API server, scheduler, and controller manager. Worker nodes host application containers, with each node containing a kubelet and container runtime. Pods represent the smallest deployable units within Kubernetes, encapsulating one or more containers that share resources. Additionally, services provide stable IP addresses and DNS names for accessing and managing groups of pods. This architecture allows for robust application management, facilitating scalability and resilience.
Benefits of Cloud Native DevOps with Kubernetes
Cloud native DevOps with Kubernetes offers numerous advantages for modern software development, enhancing efficiency and operational performance.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability becomes effortless with Kubernetes, as it allows applications to expand according to varying workloads. Kubernetes supports horizontal scaling, enabling teams to add more containers as demand increases. In contrast, reducing resources during off-peak times helps in optimizing costs effectively. Flexibility stands out with Kubernetes, as it accommodates various environments, whether on-premises or across multiple cloud providers. Teams can quickly deploy applications on any infrastructure, allowing for seamless integration and adaptability to changing requirements.
Enhanced Collaboration
Collaboration thrives in cloud native DevOps environments. Kubernetes encourages communication between development and operations teams through shared tools and practices. Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines facilitate faster feedback loops. Teams can address issues collaboratively, promoting a culture of accountability and ownership over application performance. Tools integrated with Kubernetes foster real-time visibility into project progress, allowing for swift adjustments. Ultimately, this collaborative approach leads to improved reliability and faster delivery of high-quality software.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Native DevOps
Implementing cloud native DevOps requires strategic practices that enhance efficiency and collaboration. These best practices focus on automation and reliability, ensuring seamless application management.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Establishing CI/CD pipelines is essential for automating testing and deployment of code changes. Teams benefit from reduced cycle times, accelerating the path from development to production. Automation minimizes manual processes and errors, leading to increased reliability. Frequent code integration fosters collaboration between development and operations. Each integration triggers automated tests, ensuring code quality and function. This systematic approach enables rapid feedback, helping teams address issues swiftly and maintain product standards.
Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging provide critical insights into application performance. Effective tool integration allows teams to track metrics, manage system health, and detect anomalies in real time. Utilizing dashboards facilitates visibility into application behavior and resource utilization. Anomaly detection systems alert teams before user experience suffers, enabling proactive resolution. Comprehensive logging supports auditing and troubleshooting efforts. By maintaining an observability strategy, organizations can continuously enhance application reliability and performance.
Challenges and Solutions in Cloud Native DevOps
Cloud native DevOps faces varying challenges, particularly in its implementation with Kubernetes. Addressing these obstacles becomes essential for optimal performance and efficiency.
Common Obstacles
Complexity in managing microservices presents a significant hurdle. It often leads to difficulties in service communication and orchestration. Container sprawl arises when organizations deploy numerous containers across multiple environments, complicating management and monitoring. Many teams struggle with skill gaps, as expertise in Kubernetes and cloud native practices can be limited. Security concerns frequently arise, particularly in safeguarding data across distributed systems. Additionally, integrating legacy systems with cloud-native architecture poses challenges, slowing down overall progress.
Overcoming Challenges
Adopting best practices streamlines the process. Effective training programs enhance team skills in Kubernetes and cloud-native technologies, empowering improved management. Employing robust monitoring solutions addresses container sprawl and tracking issues. Implementing service mesh technologies simplifies service communication and enhances observability across microservices. Security best practices, such as automated vulnerability scanning and policy enforcement, mitigate risks. Finally, leveraging API gateways facilitates smoother integration of legacy systems, enabling a seamless transition to cloud-native environments.
Adopting cloud native DevOps with Kubernetes transforms the software development landscape. By leveraging Kubernetes’ robust features, teams can enhance their agility and streamline processes, ultimately delivering high-quality applications faster. The integration of CI/CD pipelines fosters collaboration and accountability, ensuring that development and operations work hand in hand.
As organizations navigate the complexities of cloud native environments, embracing best practices becomes essential. By focusing on automation, monitoring, and continuous improvement, teams can overcome challenges and maximize the benefits of Kubernetes. This approach not only optimizes resource usage but also drives innovation, making cloud native DevOps a critical component for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s competitive market.




